Research Highlights
Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex
A protein containing a metal complex for blue paint inhibits growth of a pathogenic bacterium through iron deprivation
Abstract:
Professor Yoshihito Watanabe (WPI-ITbM, Cooperating Researcher), Associate Professor Osami Shoji, Ms. Chikako Shirataki of Nagoya University and co-workers have found a new method using an artificial metalloprotein (a protein that contains a metal) to inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria, which is a common bacterium that can cause diseases in humans and evolves to exhibit multiple antibiotic resistance. The inhibition of growth has been achieved through the deprivation of iron uptake using an artificial metalloprotein.
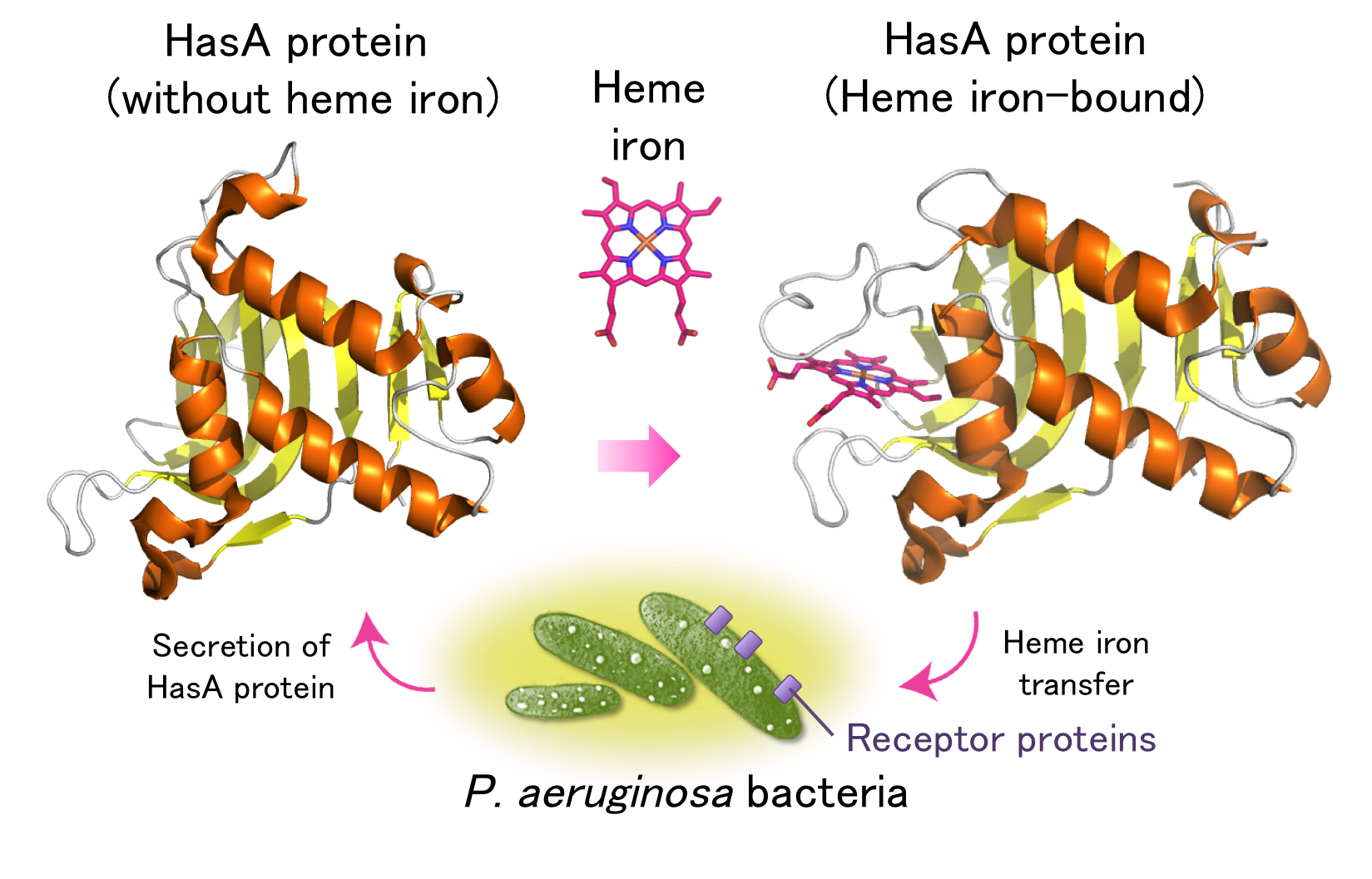
Figure 1. Heme iron capturing mechanism of P. aeruginosa bacteria by HasA protein.
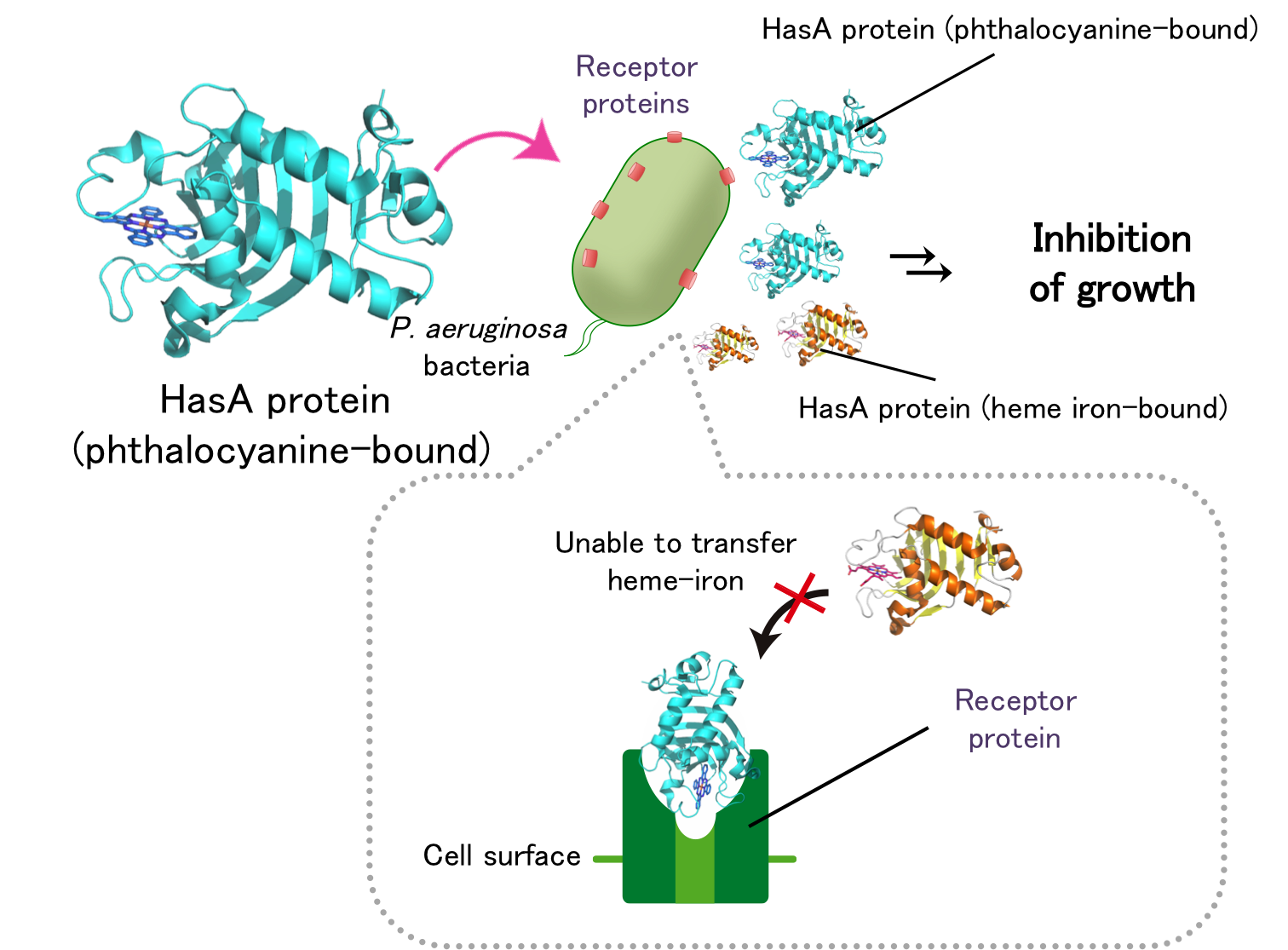
Figure 2. Inhibition of heme iron uptake of P. aeruginosa by phthalocyanine-bound HasA protein.
Journal Information:
"Inhibition of Heme Uptake in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by its Hemophore (HasAp) Bound to Synthetic Metal Complexes" Chikako Shirataki, Osami Shoji, Mitsuyoshi Terada, Shin-ichi Ozaki, Hiroshi Sugimoto, Yoshitsugu Shiro, Yoshihito Watanabe, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2014). The article was selected as an inside cover.
Links:
- Press Release
- Nagoya University Research
- ResearchSEA "Blue paint on Japanese bullet trains can inhibit bacteria growth" (March 3, 2014)
- Phys.Org "Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex", e! Science News (March 5, 2014)
- Innovations Report "Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex" (March 5, 2014)
- Science Daily "Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex" (March 6, 2014)
- Cleanroom Technology "Blue paint on Japanese bullet trains can inhibit bacteria growth" (March 7, 2014)
- Scicasts "Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex" (March 7, 2014)
- Read Medical News "Combatting hospital-acquired infections with protein metal complex" (March 7, 2014)
- design products & applications "Blue paint on Japanese bullet trains can inhibit bacteria growth" (March 9, 2014)
- chemistry2011.org "Blue paint on Japanese bullet trains can inhibit bacteria growth"
- Lab Bulletin "Blue paint on Japanese bullet trains can inhibit bacteria growth" (March 19, 2014)
- Asian Scientist "Blue Paint On Bullet Trains Can Inhibit Bacterial Growth" (March 21, 2014)
- Digital Journal "Why many Japanese bullet trains are about to go blue" (March 25, 2014)
- RailNews "Japan to use Specially prepared Anti-bacterial Blue Paint on Bullet Trains" (March 31, 2014)
Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry -Watanabe Group-:
http://bioinorg.chem.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/index.html
Media Coverage and Related Links:
2014-03-03

